|
|
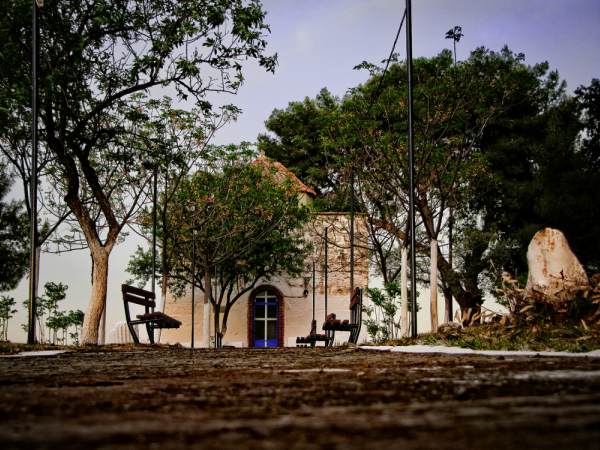
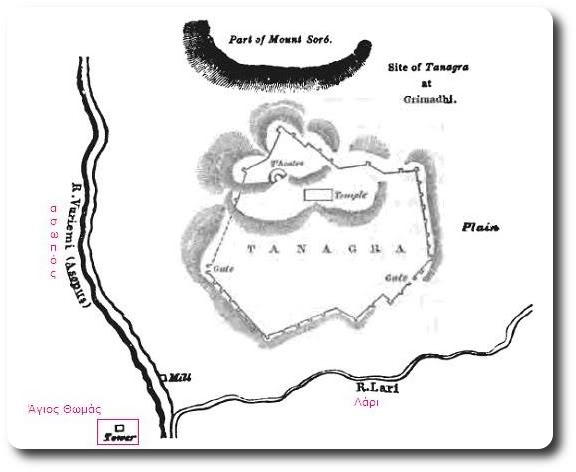
Churches> Saint Thomas ----------------------------------------------------------------- Historical chapel near Asopos River. It is sacred to Saint Thomas, genius Loci of the village. Tradition wants the Saint to protect the villagers from the bubonic plague that had spread the district. So they honored him by giving his name to the village. In Greek: Ayios Thomas. According to Leiden University research, the chapel is considered mid Byzantine (12th century). the cupola is posterior. Ancient Tanagra lies opposite to the chapel. ----------------------------------------------------------------- According to Schachter McGill, the chapel is considered first christian basilica of the 10th century. By the time Byzantine Empire reconquered Boeotia from slaves, starts a period of steady growth of rural population. The small hamlets take the role of ancient Tanagra. During crusades the district pases under the commandership of a Frank lord who converts the chapel into feudal chateau. (13th century). ----------------------------------------------------------------- 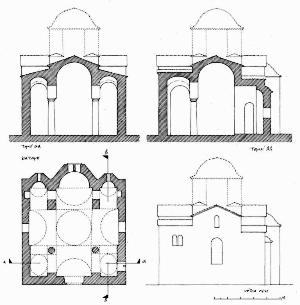 The temple of Ag.Thomas is built near the bridge Assopos, crossed by the road leading from the highway: Athens-Lamia to the village Ag.Thomas(Liatani).
To the west rises the hill of ancient Tanagra and the memorial is located on elevated grounds, in a dominant position in the valley of Asopia. The temple of Ag.Thomas is built near the bridge Assopos, crossed by the road leading from the highway: Athens-Lamia to the village Ag.Thomas(Liatani).
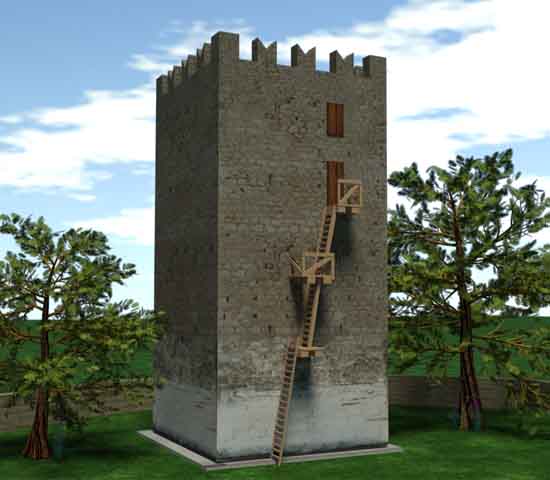
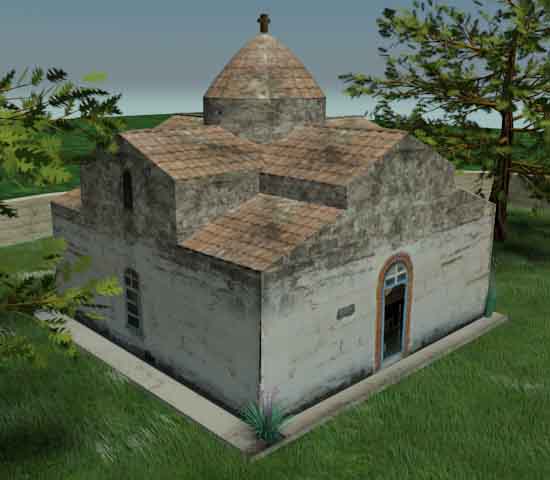
To the west rises the hill of ancient Tanagra and the memorial is located on elevated grounds, in a dominant position in the valley of Asopia.The peculiarity of the monument is that presents cubic external form with nearly flat roof and small protruding dome. This format is the lower part of ruined tower,, which was incorporated into the preexisting temple. The original form of the church is indicated by traces of roofs, exposed mainly in western and east side only, which provide the possibility of a secure graphical rehabilitation. The temple belongs to the simple two-columned cruciform with a dome with a wider dating to the 12th century, who probably built in the early Christian position. The plan is almost square (7.88 X 7.76m) and housing the eastern flats made with semi-cylindrical vaults, while the western with downcast oven styles. The area of the sanctuary includes three prominent hexagonal niches, of which the middle is illuminated with bilobed window with marble pillars, while the other two with smaller lobed windows. The main entrance of the church, has been processed, formed with petalomorfo bow, while the north and south exposures by a large arched window with red brick frame. Externally, on the left of the entrance is fitted didialekti ancient inscription in black marble, signed KAFISIAS EPOEISE. On the south side appears closed today, bilobed limestone window positioned at height. The Middle Byzantine iconostasis was replaced with an Ottoman era built, with frescoes of 20th century which are the only that can be seen indide the church. Parts of the original temple (small columns, cornice) saved previously scattered in the temple and its courtyard. Externally, the western side of the church throughout its length, bounded by large stones, the base of a space like a splint with three openings. The walls of the church are mixed using normal spolia the base and corners, and cloisonne structure, typical of the Middle Byzantine period, from then on top. Semi-procesed stones placed in horizontal rows with vertical joints filled with vertical bricks, Koufos form Greek letters and pseudokoufik decorations. Greater care building appears in the recesses of eastern side with hewn stones and symmetric contour placement deaf. The walled precinct of the temple stand scattered many ancient states apparently the church, and dark gravestones from titanolitho. to the northwest preserved vaulted tomb with embedded cop. 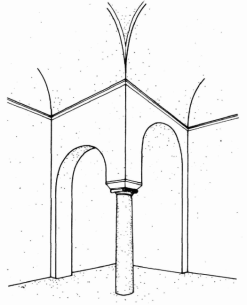 The incorporation of the church into a taller building that probably functioned as
chorodespotikos tower was during Frank (14th), to
surveillance of farmland underside plain Assopos where there were other
similar. In this phase was important changes in its interior, but
likely to change the use of the sanctuary at least as chapel. With
this format is detected and by Leake in the early 19th century, by which, however,
referred to as Frankish tower was converted into a church.
Generally, most references are to the monument with respect to the adjacent Asopus
and the cop which are embedded in it, and especially the aforementioned
inscribed plaque, which attracted the interest of antiquity surfers
19th century.
Until about 1900 as mentioned by Baedeker, the monument retains the form
tower, while its current form should be acquired between 1900 and 1930, when
removed a substantial part of the material in order to be used for demolition
the construction of the road leading to the village. Since then it has undergone many repairs
in an attempt ware and thefts.
Typological features of Ag.Thoma is anisostathmia housing
between the east and west because of oven housing
the latter, the Kufic decorations, double-light windows with limestone within the
petalomorfo bow entry, bilobed window of the sanctuary.
The monument was restored in form, after removal of supplements to faces
and restoring the original appearance of the dome, showing an elaborate and rich
construction funerary chapel or not the Middle Byzantine period.
From its elements dating from the mid 12th century and is associated with
provincial monuments of the same period, Greek press, but with some special intentions
mainly in the inner space, and must be integrated into a period of continuity
construction activities of the century in the region of Thebes.
The incorporation of the church into a taller building that probably functioned as
chorodespotikos tower was during Frank (14th), to
surveillance of farmland underside plain Assopos where there were other
similar. In this phase was important changes in its interior, but
likely to change the use of the sanctuary at least as chapel. With
this format is detected and by Leake in the early 19th century, by which, however,
referred to as Frankish tower was converted into a church.
Generally, most references are to the monument with respect to the adjacent Asopus
and the cop which are embedded in it, and especially the aforementioned
inscribed plaque, which attracted the interest of antiquity surfers
19th century.
Until about 1900 as mentioned by Baedeker, the monument retains the form
tower, while its current form should be acquired between 1900 and 1930, when
removed a substantial part of the material in order to be used for demolition
the construction of the road leading to the village. Since then it has undergone many repairs
in an attempt ware and thefts.
Typological features of Ag.Thoma is anisostathmia housing
between the east and west because of oven housing
the latter, the Kufic decorations, double-light windows with limestone within the
petalomorfo bow entry, bilobed window of the sanctuary.
The monument was restored in form, after removal of supplements to faces
and restoring the original appearance of the dome, showing an elaborate and rich
construction funerary chapel or not the Middle Byzantine period.
From its elements dating from the mid 12th century and is associated with
provincial monuments of the same period, Greek press, but with some special intentions
mainly in the inner space, and must be integrated into a period of continuity
construction activities of the century in the region of Thebes.Sorce: Simatou Α. Μ., Christodoulopoulou R., "Agios Thomas Tanagras", Lampidon. Athens 2003. figures: Chr. Boura, Attica's churches ----------------------------------------------------------------
Source: Travels in Northern Greece. William Martin Leake, 1835
-----------------------------------------------------------------
Recorded and digitally reconstructed under the direction of Chiara Piccoli (Leiden University) and with the assistance of Chrystalla Loizou (University of Cyprus) and Katerina Ragkou (University of Cologne) -------------------------------------------------------
-------------------------------------------------------
-------------------------------------------------------
------------------------------------------------------- |
||||||||||
|
1999-2018, Saint Tomas Improvement Team - Contact:agios | |||||||||||